Leitschichtdicke δ
Äquivalente Leitschichtdicke, Eindringmaß, Eindringtiefe, Skin-Tiefe, Stromeindringtiefe
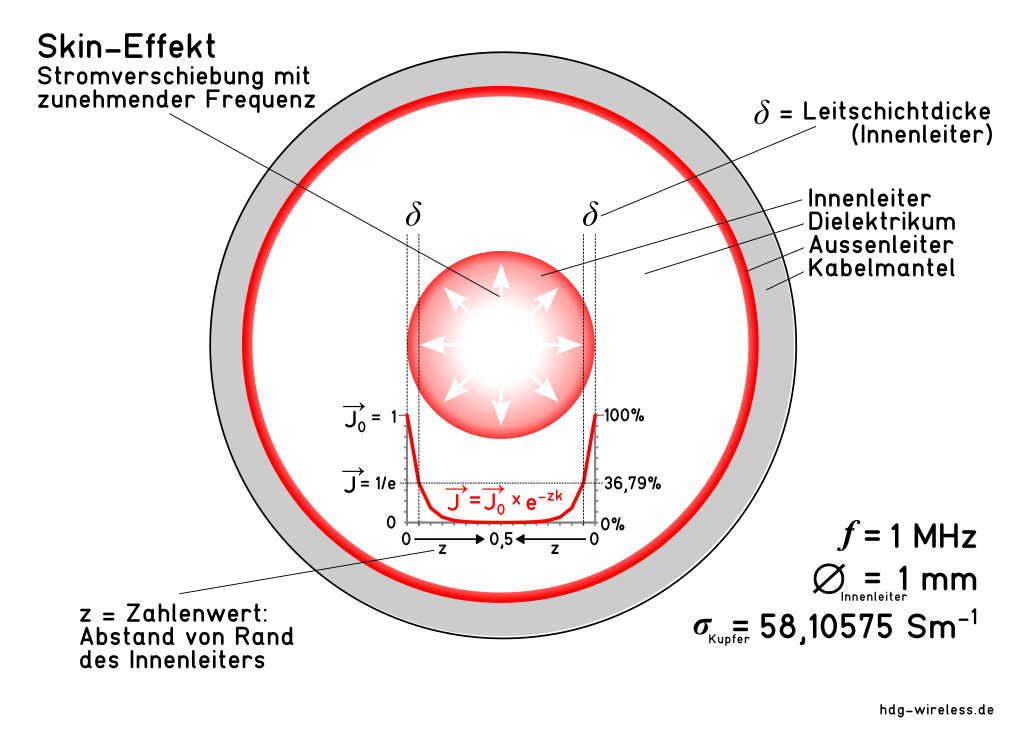
Die äquivalente Leitschichtdicke δ ist der Abstand vom Rand des Leiters zu der Stelle des Leiterquerschnitts, an dem durch den Skin-Effekt die Feldstärke einer elektromagnetischen Welle um den Faktor 1/e (36,79 %) abgenommen hat, und stellt somit die Dicke (Skin-Tiefe) der äquivalent elektrisch leitenden Kreisringfläche A⊚ (äquivalente Fläche A) des Leiters bei hochfrequentem Wechselstrom dar.
Leitschichtdicke:
δ = Leitschichtdicke [m]
k = Dämpfungsfaktor (Stromeindringtiefe) [m-1]
R = Radius (Radius Leiter) [m]
r = Radius (Radius bis Leitschichtdicke) [m]
ρ = spezifischer Widerstand [Ωm]
ω = Kreisfrequenz [s-1]
µ = Permeabilität [Hm-1]
µ0 = Magnetische Feldkonstante [NA-2]
µr = Relative Permeabilität [1]
π = Kreiszahl (Pi) [1]
f = Frequenz [Hz]
σ = elektrische Leitfähigkeit [Sm-1]
Diese Gleichung beschreibt die Dicke des effektiv genutzten Leitungsquerschnitts eines fiktiven Volldraht-Ersatzleiters.
Im Gegensatz zur gleichmäßigen Verteilung der Stromdichte über den Querschnitt eines Leiters bei Gleichstrom ist mit zunehmender Frequenz des Wechselstroms eine Dichteverlagerung hin zum Randbereich des Leiters zu beobachten.
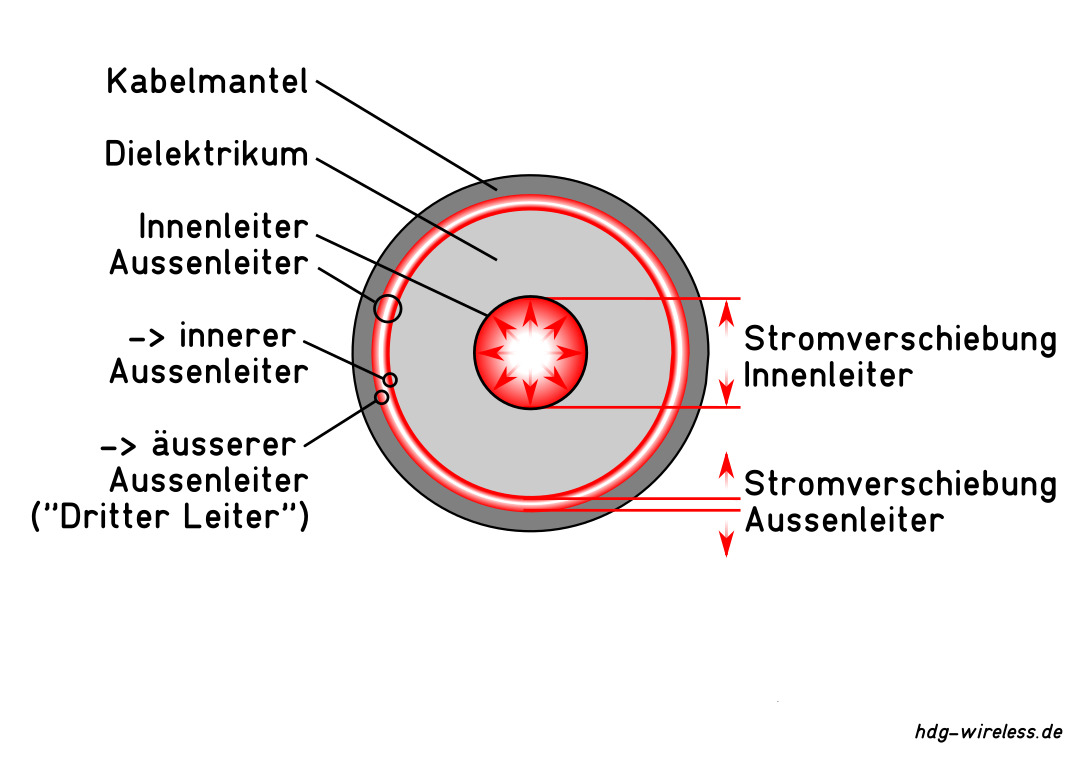
Beim Skin-Effekt findet der Stromfluss mit zunehmender Frequenz f des Wechselstroms ≂ in einer immer dünner werdenden Schicht an der Oberfläche (Skin) des Leiters statt.
Die Stromdichte im Inneren des Leiters ist bei Gleichstrom gleichmäßig über den Querschnitt eines Leiters verteilt.
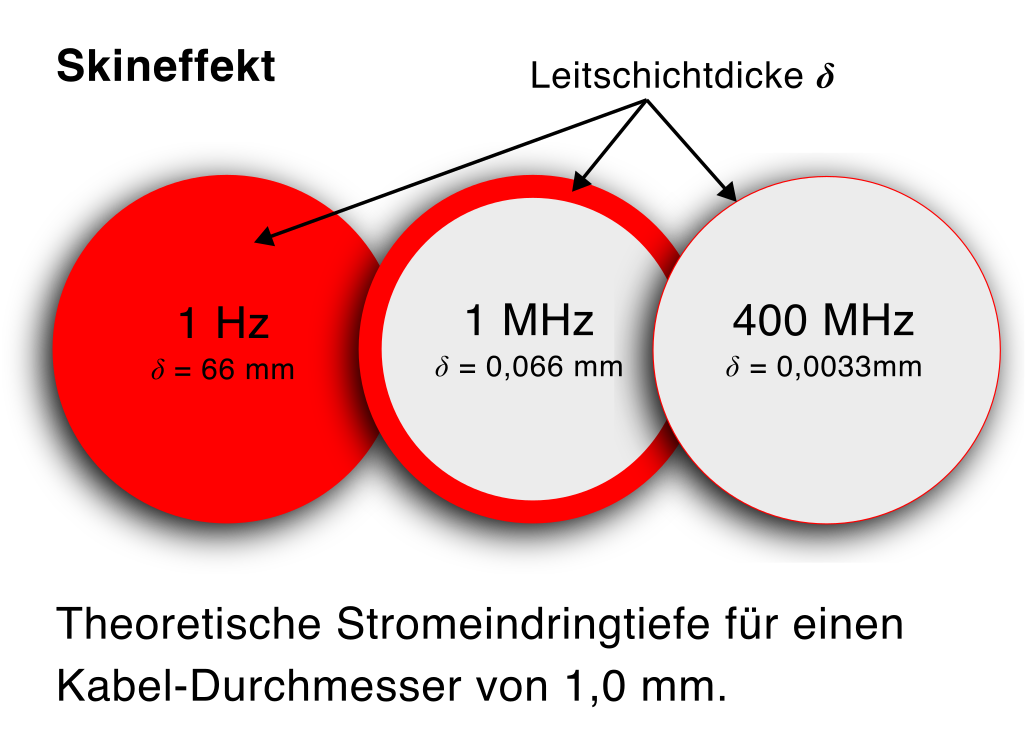
Bei Wechselstrom nimmt die Stromdichte exponentiell mit dem Abstand von der Oberfläche ab, bzw. die äquivalente Leitschichtdicke (Skin-Tiefe, Stromeindringtiefe) verringert sich.

δ = Leitschichtdicke [m]
J→ = vektorielle Stromdichte [tba.]
e = Eulersche Zahl [1]
z = Zahlenwert [1]
k = Dämpfungsfaktor (Stromeindringtiefe) [m-1]
f = Frequenz [Hz]
σ = elektrische Leitfähigkeit [Sm-1]
Für die Berechnung der Kreisringfläche A⊚ kann für sehr kleine Leitschichtdicken (δ ≪ r) im Verhältnis zum Radius, also hochfrequente Signale, in Näherung die folgende Formel herangezogen werden:
A⊚ = Kreisringfläche [m2]
π = Kreiszahl (Pi) [1]
r = Radius [m]
δ = Leitschichtdicke [m]
Die Herleitung erfolgt über die Formel der Kreisringfläche A⊚ und die der Leitschichtdicke δ.
für δ ≪ R
⇒ A⊚ = 2πRδ
A⊚ = Kreisringfläche [m2]
π = Kreiszahl (Pi) [1]
R = Radius (Radius Leiter) [m]
r = Radius (Radius bis Leitschichtdicke) [m]
δ = Leitschichtdicke [m]
Ohmscher Widerstand Rδ
Rδ = ohmscher Widerstand (Leitschichtdicke δ ⇒ Skin-Effekt) [Ω]
l = Länge des Leiters [m]
π = Kreiszahl (Pi) [1]
r = Radius Innenleiter [m]
R = Radius Aussenleiter [m]
σ = elektrische Leitfähigkeit [Sm-1]
f = Frequenz [Hz]
µr = Relative Permeabilität [1]
µ0 = Magnetische Feldkonstante [NA-2]
d = Durchmesser Innenleiter [m]
D = Durchmesser Aussenleiter [m]
i/o = Innenleiter/Aussenleiter
| Frequenz | Leitschichtdicke | Kreisringfläche A⊚ |
Ohmscher Widerstand R |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| f | δ | (Leiter: ∅ 1mm, Länge: 1m) | ||
|
π(R2-r2)
=
π(2r-δ)δ |
2πrδ | |||
| 1 Hz | 66,03 mm | 0,78540 mm2 | --- | --- |
| 10 Hz | 20,88 mm | 0,78540 mm2 | --- | --- |
| 20 Hz | 14,76 mm | 0,78540 mm2 | --- | --- |
| 50 Hz | 9,34 mm | 0,78540 mm2 | --- | --- |
| 100 Hz | 6,60 mm | 0,78540 mm2 | --- | --- |
| 200 Hz | 4,67 mm | 0,78540 mm2 | --- | --- |
| 500 Hz | 2,95 mm | 0,78540 mm2 | --- | --- |
| 1 kHz | 2,088 mm | 0,78540 mm2 | --- | --- |
| 2 kHz | 1,476 mm | 0,78540 mm2 | --- | --- |
| 5 kHz | 0,934 mm | 0,78540 mm2 | --- | --- |
| 10 kHz | 0,660 mm | 0,78540 mm2 | --- | --- |
| 20 kHz | 0,467 mm | 0,78195 mm2 | --- | 0,01173 Ω |
| 50 kHz | 0,295 mm | 0,65373 mm2 | --- | 0,01855 Ω |
| 100 kHz | 0,209 mm | 0,51898 mm2 | --- | 0,02624 Ω |
| 200 kHz | 0,148 mm | 0,39534 mm2 | --- | 0,03711 Ω |
| 500 kHz | 0,093 mm | 0,26595 mm2 | --- | 0,05867 Ω |
| 1 MHz | 66,03 µm | 0,19373 mm2 | 0,20743 mm2 | 0,08297 Ω |
| 2 MHz | 46,69 µm | 0,13982 mm2 | 0,14667 mm2 | 0,11734 Ω |
| 5 MHz | 29,53 µm | 0,09002 mm2 | 0,09276 mm2 | 0,18553 Ω |
| 10 MHz | 20,88 µm | 0,06422 mm2 | 0,06559 mm2 | 0,26237 Ω |
| 20 MHz | 14,76 µm | 0,04570 mm2 | 0,04638 mm2 | 0,37105 Ω |
| 50 MHz | 9,34 µm | 0,02906 mm2 | 0,02933 mm2 | 0,58668 Ω |
| 100 MHz | 6,60 µm | 0,02061 mm2 | 0,02074 mm2 | 0,8297 Ω |
| 200 MHz | 4,67 µm | 0,01460 mm2 | 0,01467 mm2 | 1,17337 Ω |
| 400 MHz | 3,30 µm | 0,01034 mm2 | 0,01037 mm2 | 1,65939 Ω |
| 500 MHz | 2,95 µm | 0,00925 mm2 | 0,00928 mm2 | 1,85526 Ω |
| 800 MHz | 2,33 µm | 0,00732 mm2 | 0,00733 mm2 | 2,34673 Ω |
| 1 GHz | 2,09 µm | 0,00655 mm2 | 0,00656 mm2 | 2,62373 Ω |
| 1.8 GHz | 1,56 µm | 0,00488 mm2 | 0,00489 mm2 | 3,5201 Ω |
| 2.4 GHz | 1,35 µm | 0,00423 mm2 | 0,00423 mm2 | 4,06466 Ω |
|
f = Frequenz [Hz] |
||||
| Konstante | Wert | Einheit |
|---|---|---|
| magnetische Feldkonstante µ0 | ||
| µ0 | 1,25663706212·10-6 | NA-2 |
|
µ0 =
B0
H0
=
1
ε0c02
≈
4π·10-7
|
||
| Kreiszahl π | ||
| π | 3,1415926535898 |
1
|