Resonanz (Elektrophysik)
Mit Resonanz wird das Verschwinden des Blindwiderstands X (Reaktanz) in einer stromgespeisten Antenne bezeichnet.
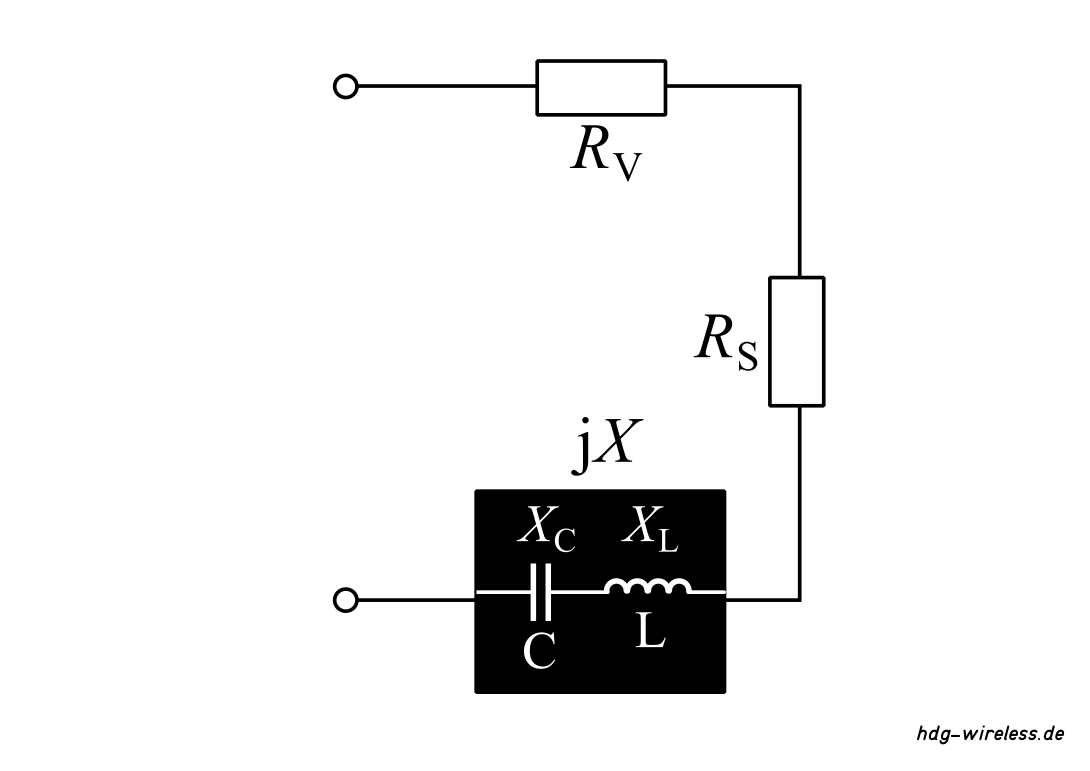
Ersatzschaltbild: Antenne (Widerstände)
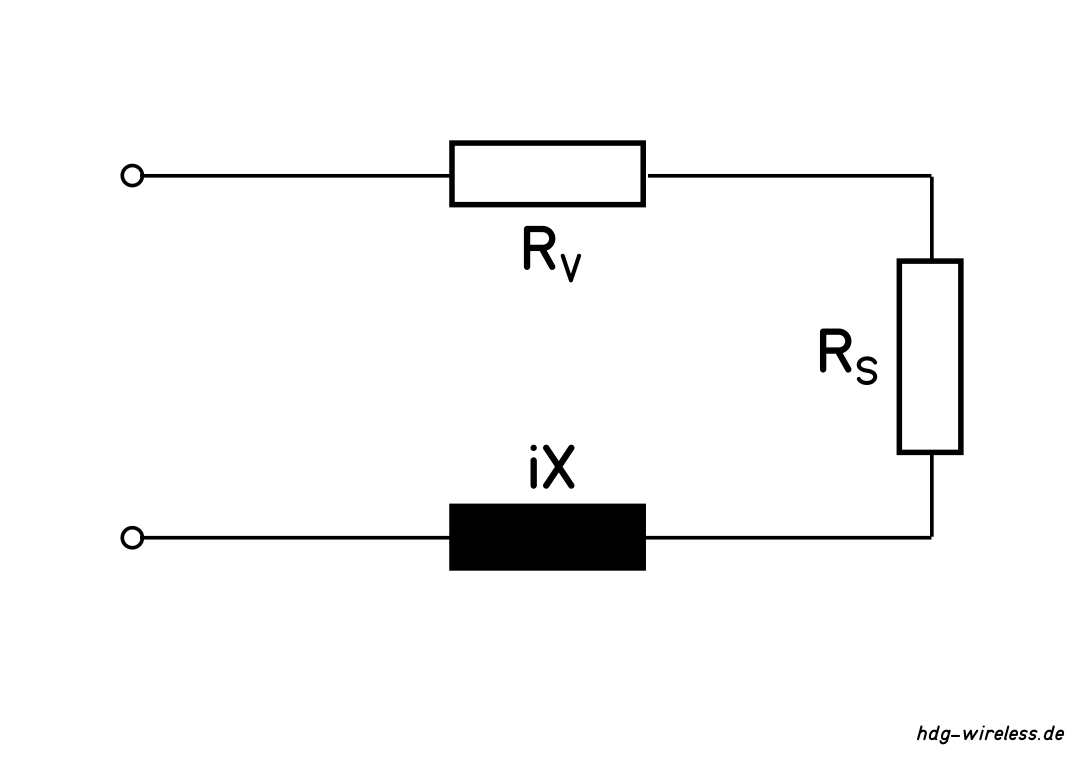
RV = Verlustwiderstand [Ω]
RS = Strahlungswiderstand [Ω]
X = Blindwiderstand [Ω]
i = imaginäre Einheit [1]
Blindwiderstand X:
X = Blindwiderstand [Ω]
XL = induktiver Blindwiderstand [Ω]
XC = kapazitiver Blindwiderstand [Ω]
Ersatzschaltbild: Antenne - System
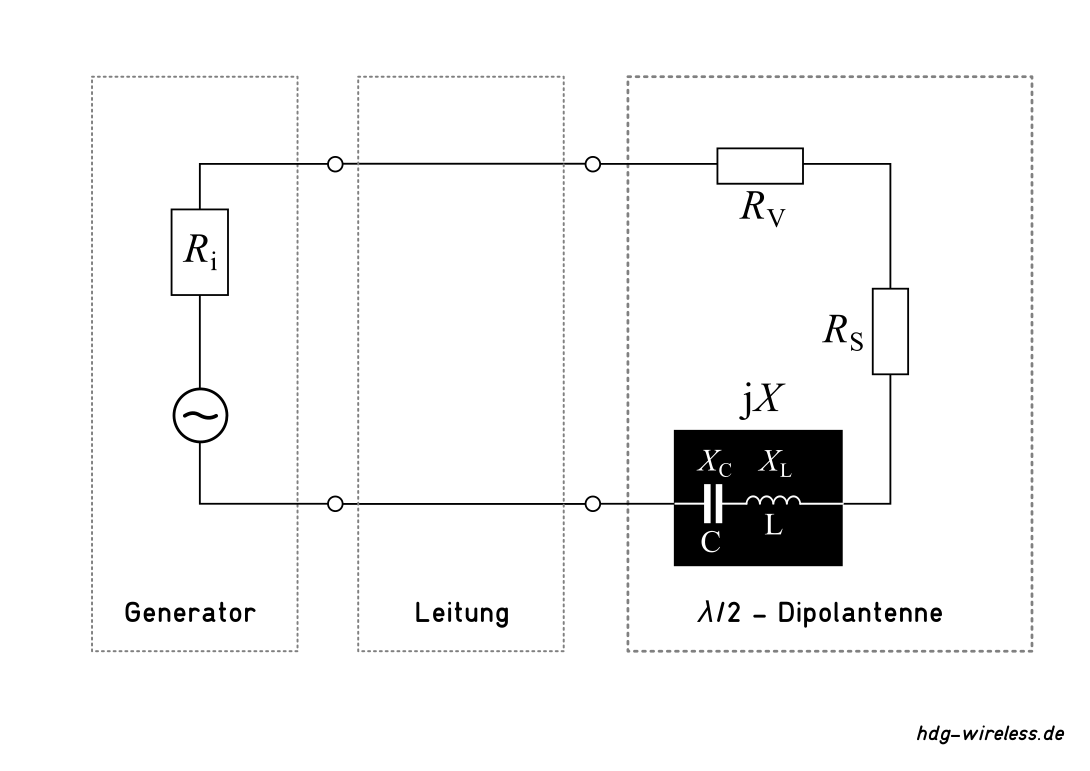
Ri = Innenwiderstand [Ω]
RV = Verlustwiderstand [Ω]
RS = Strahlungswiderstand [Ω]
j = imaginäre Einheit [1]
X = Blindwiderstand [Ω]
XL = induktiver Blindwiderstand [Ω]
XC = kapazitiver Blindwiderstand [Ω]
C = Kapazität [F]
L = Induktivität [H]
Bei Resonanz einer Antenne...
... ist der induktive Blindwiderstand XL positiv und der kapazitive Blindwiderstand XC negativ, d.h. sie sind entgegengesetzt gerichtet.
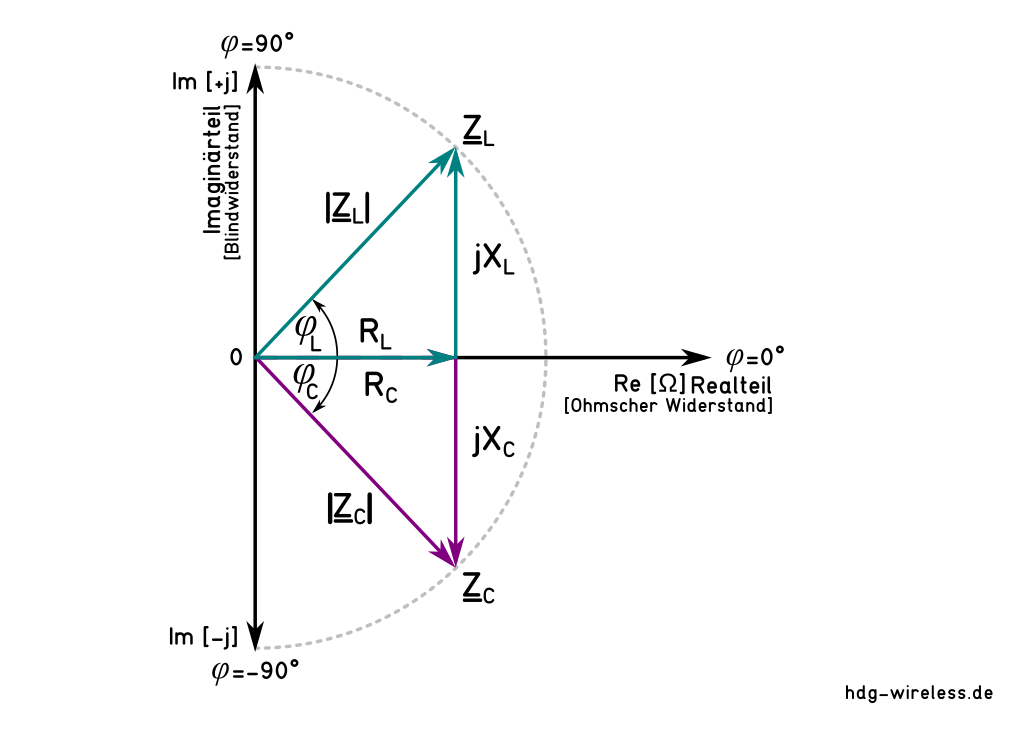
ZL = induktive Impedanz [ Ω]
ZC = kapazitive Impedanz [ Ω]
XL = induktiver Blindwiderstand [ Ω]
XC = kapazitiver Blindwiderstand [ Ω]
RL = ohmscher, induktiver Widerstand [ Ω]
RC = ohmscher, kapazitiver Widerstand [ Ω]
φ = Phasenwinkel [ rad]
... sind der induktive Blindwiderstand XL und der kapazitive Blindwiderstand XC gleich groß und heben sich auf.
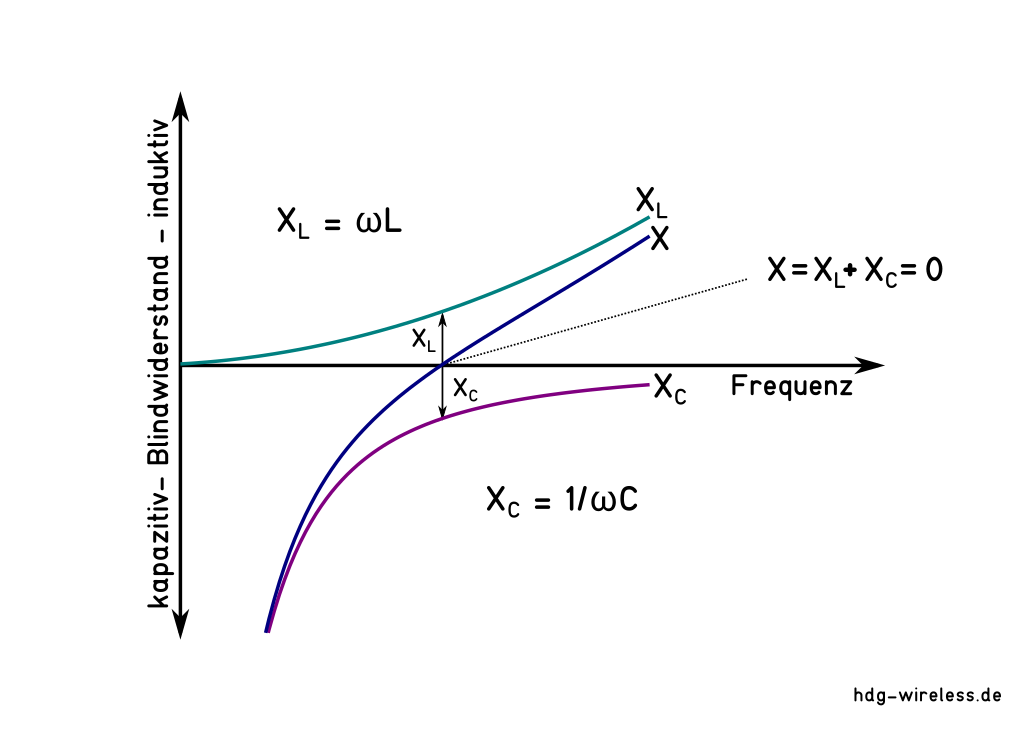
X = Blindwiderstand [ Ω]
XL = induktiver Blindwiderstand [ Ω]
XC = kapazitiver Blindwiderstand [ Ω]
L = Induktivität [ H]
C = Kapazität [ F]
ω = Kreisfrequenz [ s-1]
... sinkt der Außenwiderstand Ra auf den Strahlungswiderstand RS herab (der Verlustwiderstand RV ist vernachlässigbar klein).
(Ra = RS + RV)
Ra = Außenwiderstand [ Ω]
RS = Strahlungswiderstand [ Ω]
RV = Verlustwiderstand [ Ω]
Ist die Längenausdehnung der Antenne für die eingespeiste Frequenz f zu lang, überwiegt die Induktivität L, bei einer zu kurzen Antenne die Kapazität C.
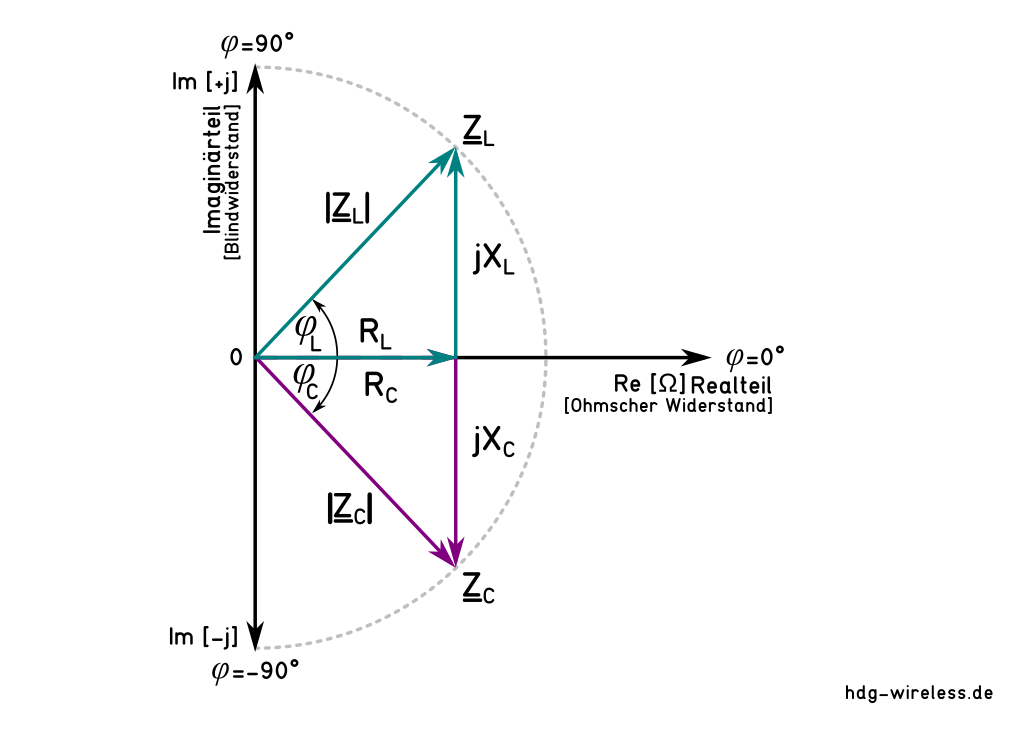
Hat die Antenne (Halbwellendipol) eine Längenausdehnung, die in etwa der halben Wellenlänge λ/2 entspricht, befindet sich der Dipol in Resonanz mit der Wellenlänge.
Unterhalb der Resonanzfrequenz f0 ist die Impedanz Z der Antenne kapazitiv:
Oberhalb der Resonanzfrequenz f0 ist die Impedanz Z einer Antenne induktiv:
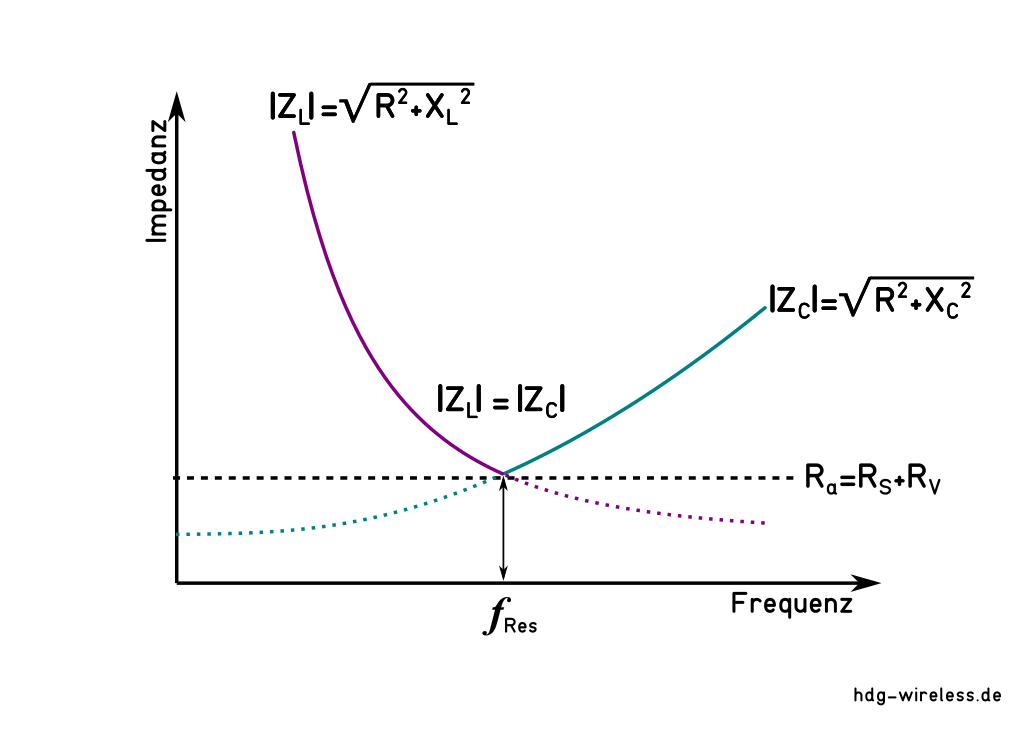
ZL = induktive Impedanz [Ω]
ZC = kapazitive Impedanz [Ω]
R = ohmscher Widerstand [Ω]
Ra = Außenwiderstand [Ω]
RV = Verlustwiderstand [Ω]
RS = Strahlungswiderstand [Ω]
XL = induktiver Blindwiderstand [Ω]
XC = kapazitiver Blindwiderstand [Ω]
f0 = Resonanzfrequenz [Hz]
Bei Resonanz wirken keine kapazitiven oder induktiven Komponenten, sondern nur der rein ohmsche Strahlungswiderstand RS.
Die Herleitung einer Dipol-Antenne aus einem LC-Schwingkreis zeigt, dass eine Antenne einen reaktiven Anteil (Schwingkreis) aufweist.
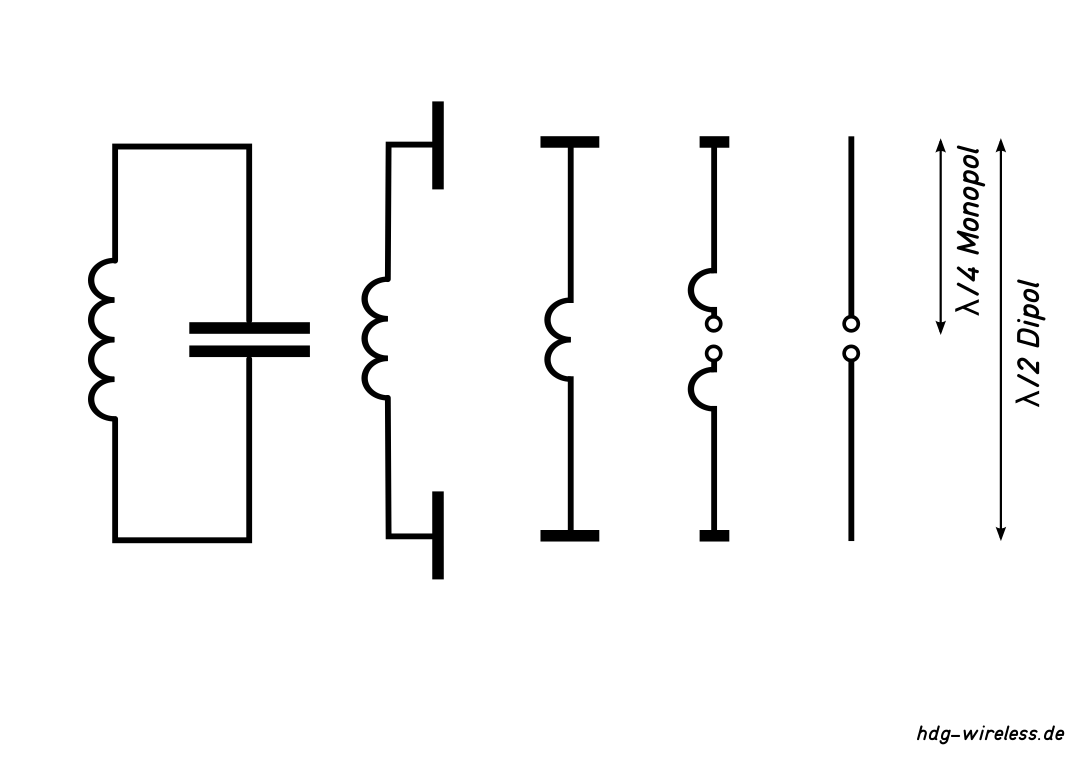
Hinzu kommt ein resistiver Anteil, der rein ohmsche Antennenwiderstand RA, der sich wiederum aus Verlustwiderstand RV und Strahlungswiderstand RS zusammensetzt.
Ersatzschaltbild: Halbwellen-Dipol
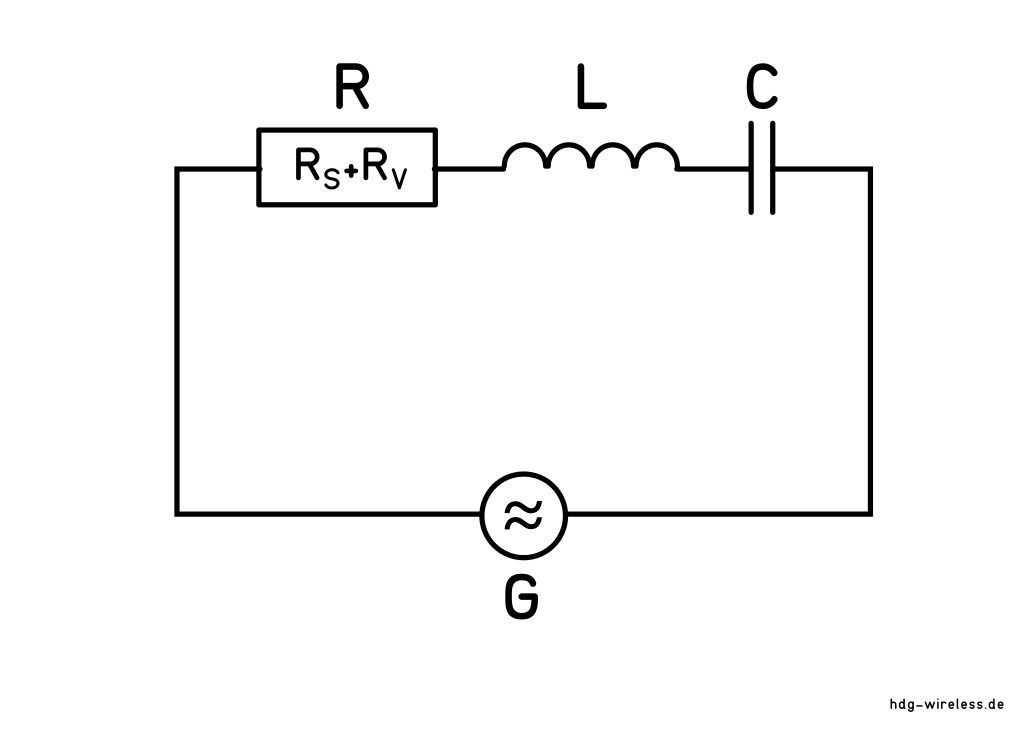
Im Resonanzfall ist die komplexe Antennenimpedanz ZA reell:
ZA = Antennenimpedanz [Ω]
RA = Antennenwiderstand [Ω]
j = imaginäre Einheit [1]
XA = Antennen-Blindwiderstand [Ω]
D.h. der Blindwiderstand X ist durch Anpassung weggestimmt und gleich Null.
Die Abstimmung erfolgt durch die Längenänderung der Antenne oder durch Kompensationsmaßnahmen in den Blindwiderständen (XC, XL).
Ersatzschaltbild: Antenne
⇒ Antenne
⇒ Blindwiderstand
⇒ Frequenz
⇒ Imaginäre Einheit
⇒ Impedanz
⇒ Induktivität
⇒ Kapazität
⇒ Reaktanz [ ⇒Blindwiderstand ]
⇒ Resonanzfrequenz
⇒ Strahlungswiderstand
⇒ Verlustwiderstand