Gütefaktor Q
Der Gütefaktor Q (≙ Güte) einer Antenne[1] ist definiert als das Verhältnis von Blindwiderstand X zum Wirkwiderstand R[2].
[1] die Antenne als Serienschwingkreis
[2] dem Strahlungswiderstand RS
Gütefaktor:
QDipol = Gütefaktor (Dipol) [1]
X = Blindwiderstand [Ω]
RS = Strahlungswiderstand [Ω]
ω = Kreisfrequenz [s-1]
L = Induktivität [H]
C = Kapazität [F]
DF = Dämpfungsfaktor [1]
f0 = Resonanzfrequenz [Hz]
Δf = Frequenzbandbreite [Hz]
f0 = Resonanzfrequenz [Hz]
fc1 = untere Grenzfrequenz [Hz]
fc2 = obere Grenzfrequenz [Hz]
Ersatzschaltbild: Halbwellendipol
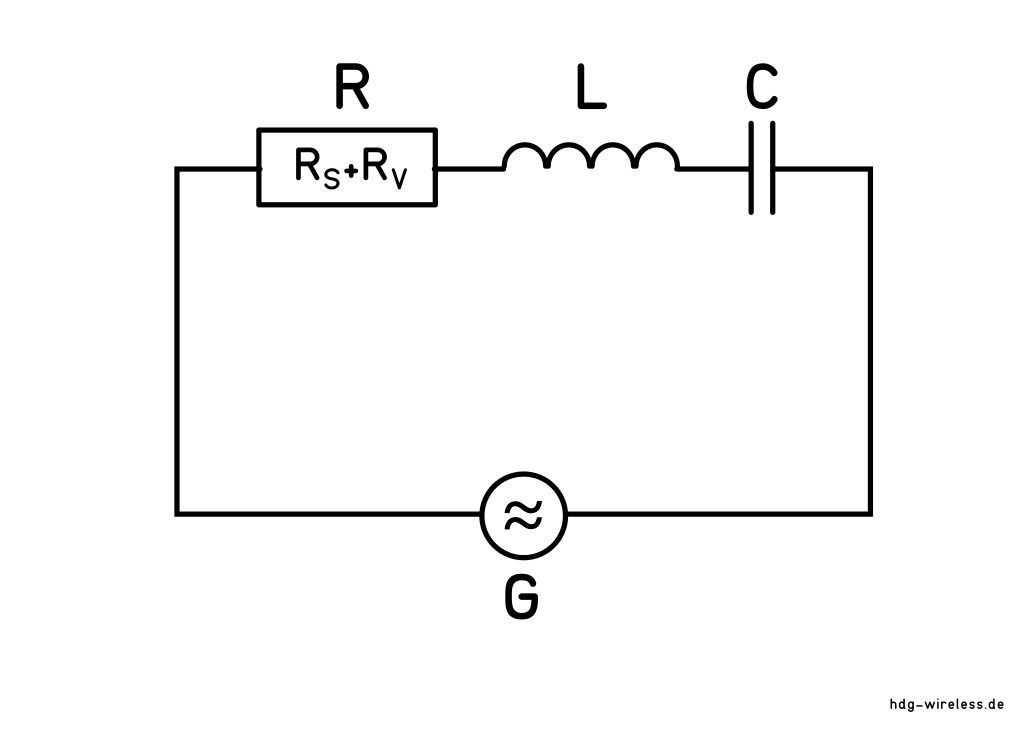
R = ohmscher Widerstand [Ω]
RV = Verlustwiderstand [Ω]
RS = Strahlungswiderstand [Ω]
L = Induktivität [H]
C = Kapazität [F]
Ableitung: Farad
1 F = 1Ableitung: Henry
1 H = 1Ableitung: Ohm
1 Ω = 1
⇒ Blindwiderstand
⇒ Dämpfungsfaktor
⇒ Dämpfungsfaktor [ ⇒Dämpfungsfaktor Eindringtiefe ]
⇒ Frequenzbandbreite
⇒ Grenzfrequenz
⇒ Induktivität
⇒ Kapazität
⇒ Kreisfrequenz
⇒ Resonanzfrequenz
⇒ Strahlungswiderstand
⇒ Wirkwiderstand [ ⇒Ohmscher Widerstand ]